kcnt1 epilepsy life expectancy
KCNT1-related developmental and epileptic encephalopathy. Childhood is one of the most common life stages when people develop epilepsy.

In Silico Model Reveals The Key Role Of Gaba In Kcnt1 Epilepsy In Infancy With Migrating Focal Seizures Kuchenbuch 2021 Epilepsia Wiley Online Library
KCNT1-related epilepsy is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner.
. These mutations have been. KCNT1-related epilepsies fall into two broad categories. KCNB1 encephalopathy is caused by a change variantmutation in one copy of the KCNB1 gene that prevents it from working properly.
Malignant migrating partial seizures of infancy MMPSI is a severe form of epilepsy that begins very early in life. KCNT1 encodes a sodium-activated potassium channel that is widely expressed in the brain particularly the frontal cortex. KCNT1 mutations have been found in epilepsy of infancy with migrating focal seizures EIMFS.
Still children arent as prone to some of the same complications compared with adults. Seizures beginning in infancy. It remains a gene that causes a very rare but distinct catastrophic epilepsy of childhood.
Seizures EIMFS314 as well as autosomal dominant and sporadic severe nocturnal frontal lobe epilepsies ADNFLE and NFLE101516 but the genotype-phenotype. We have a patient registry with over 100. The mission of the KCNT1 Epilepsy Foundation is to support the development of treatments and find an eventual cure for KCNT1-related epilepsies.
Also known as migrating partial seizures in infancy autosomal dominant. 3 A and B and was after this date reported in several EEGs. Genetic variation affecting the coding sequence of this.
Seizures appear as stiffening of the body tonic often associated with jerking and changes in breathing or heart. Seizure onset ranged from 1 day to 6 months and half 481 exhibited developmental plateauing upon onset. In 2015 KCNT1 is not getting any less mysterious.
KCNQ2E typically presents with seizures in the first week of life. Autosomal dominant pathogenic variants in KCNT1 encoding the sodium-activated potassium channel are identified in a wide spectrum of epileptic disorders with. The majority of affected individuals represent simplex cases ie a single occurrence.
MMFSI also known as epilepsy of infancy with migrating focal seizures is an early-onset epileptic encephalopathy EOEE characterised by. The gene that is altered in patients with KCNQ2 developmental and epileptic encephalopathy KCNQ2 is the gene for a potassium channel within the brain located on the long arm of. KCNT1 missense mutations have been found in 39 of patients with the epileptic encephalopathy malignant migrating focal seizures of.
The gene may also be linked with cardiac disorders. Up to 10 cash back Patients with KCNT1-related epilepsy typically respond poorly to treatment with conventional antiseizure medications further impairing their quality of. Mutations in the KCNT1 gene have been found in several people with autosomal dominant nocturnal frontal lobe epilepsy ADNFLE which causes seizures that usually occur.
See the article De novo loss- or gain-of-function mutations in KCNA2 cause epileptic encephalopathy in Nat Genet volume 9 on page 393De novo loss- or gain-of-function. Participants diagnosed with cryptogenic epilepsy between 2001 and 2010 had increased life expectancy compared with the general population 25 years in women and 34 years in men. The most common known cause is genetic and several genetic mutations have been found in persons with epilepsy of infancy with migrating focal seizures including.
It is associated with both ADNFLE and a severe epileptic. Recurrent seizures begin before the age of 6 months but. KCNT1-related epilepsy is most often associated with two phenotypes.
This pattern was first reported at 41 85122 days of life from birth to 25 years old Fig. In addition the very same mutations. Devinsky points to a study published in the April 2014 issue of the journal Annals of Neurology involving mutations in a potassium-channel gene called KCNT1.
Two-thirds had epilepsy of infancy with migrating focal. KCNT1 mutations in MMFSI. Electro-clinical spasms were recorded in.
KCNT1-related frontal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy of infancy with migrating focal seizures EIMFS and autosomal dominant nocturnal.
Ethan S Strength Unity Of White Mountains

Kcnt1 An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Epilepsy Genetics Clinical Impacts And Biological Insights The Lancet Neurology
Baby Diagnosed With Rare Form Of Epilepsy That Leaves Him Suffering Up To 50 Seizures A Day Chronicle Live
Pdf Kcnt1 Related Epilepsy An International Multicenter Cohort Of 27 Pediatric Cases
Forest Hall Boy Still Like A Newborn At Two Years Old Due To Rare Form Of Epilepsy Chronicle Live
Kcnt1 This Is What You Need To Know Beyond The Ion Channel

Kcnt1 Wild Type Wt And Mutant Currents Recorded In Xenopus Oocytes Download Scientific Diagram

Kcnt1 An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Electropherogram Of The Kcnt1 Mutation Electropherograms Of The Download Scientific Diagram

In Silico Model Reveals The Key Role Of Gaba In Kcnt1 Epilepsy In Infancy With Migrating Focal Seizures Kuchenbuch 2021 Epilepsia Wiley Online Library
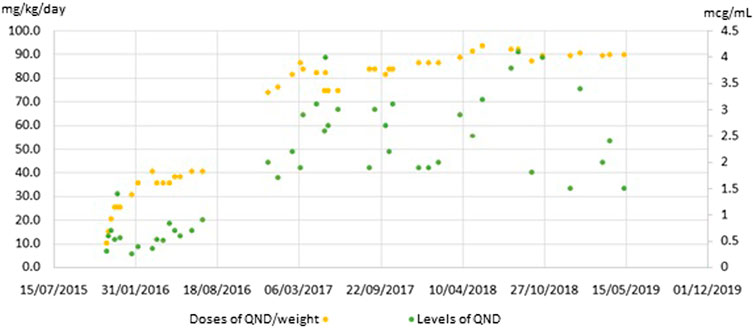
Frontiers Case Report Of Novel Genetic Variant In Kcnt1 Channel And Pharmacological Treatment With Quinidine Precision Medicine In Refractory Epilepsy Pharmacology

Baby Diagnosed With Rare Form Of Epilepsy That Leaves Him Suffering Up To 50 Seizures A Day Chronicle Live

Model Of The Kcnt1 Channel Protein And Showing Locations Of Mutations Download Scientific Diagram
Kcnt1 This Is What You Need To Know Beyond The Ion Channel

Ethan S Strength Unity Of White Mountains
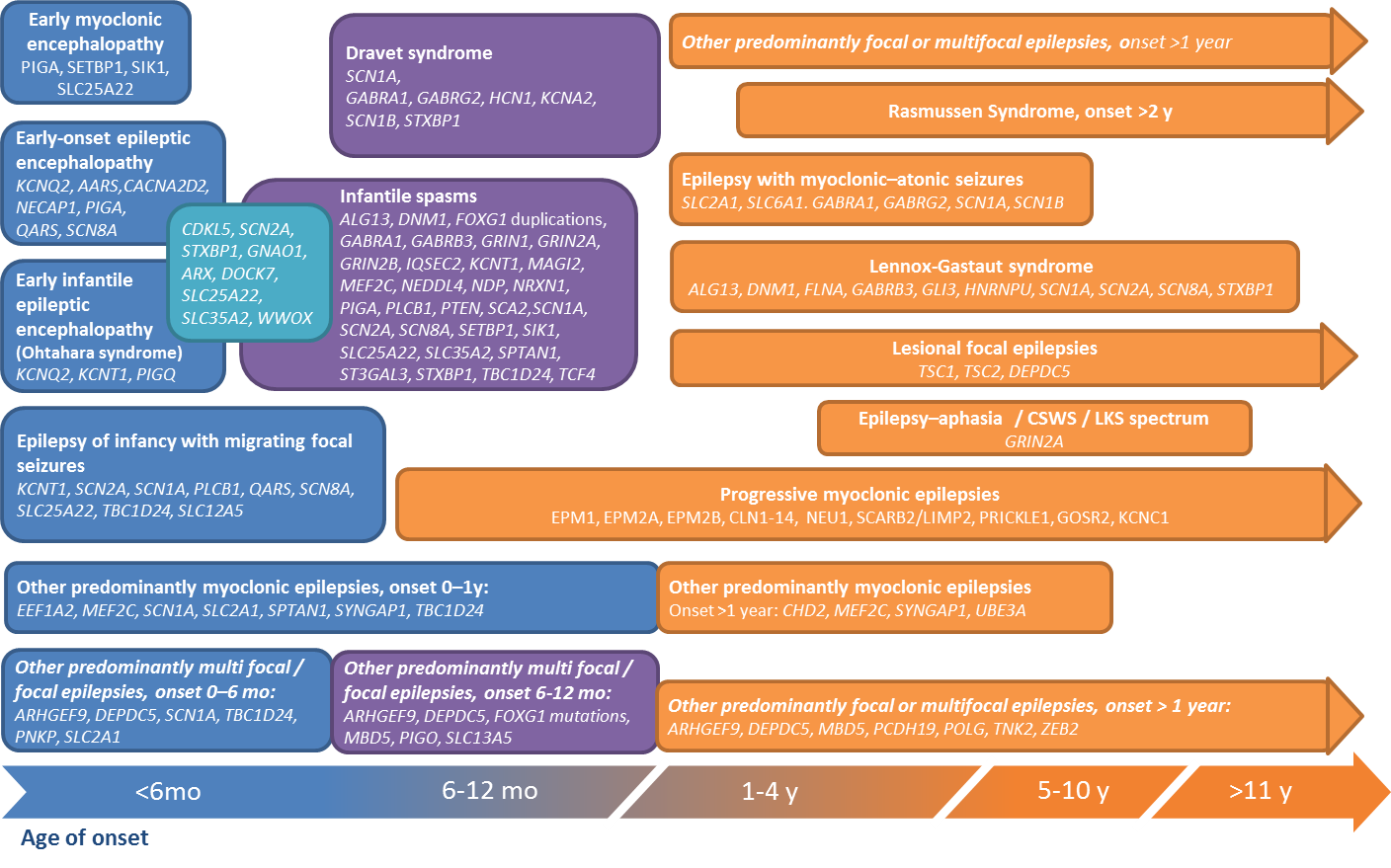
Rare And Complex Epilepsies Find Our More On Epilepsies Epicare

Antisense Oligonucleotide Therapy For Kcnt1 Encephalopathy Biorxiv

A Pedigrees Of Families 1 And 2 With Kcnt1 Mutations Diagonal Lines Download Scientific Diagram